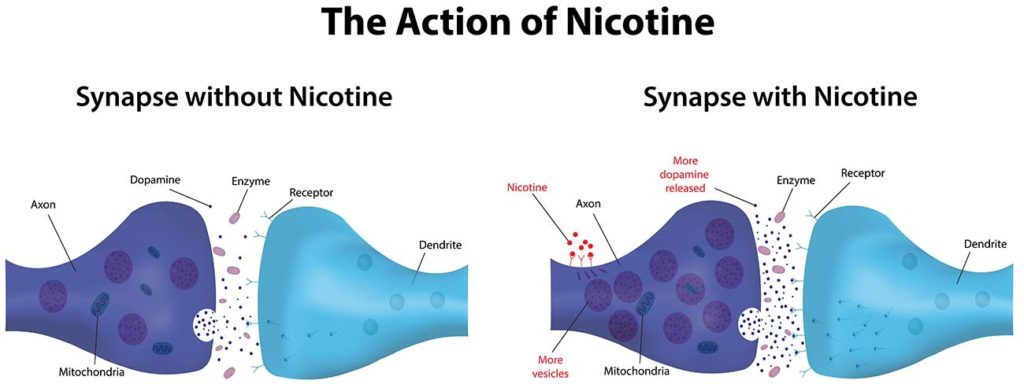
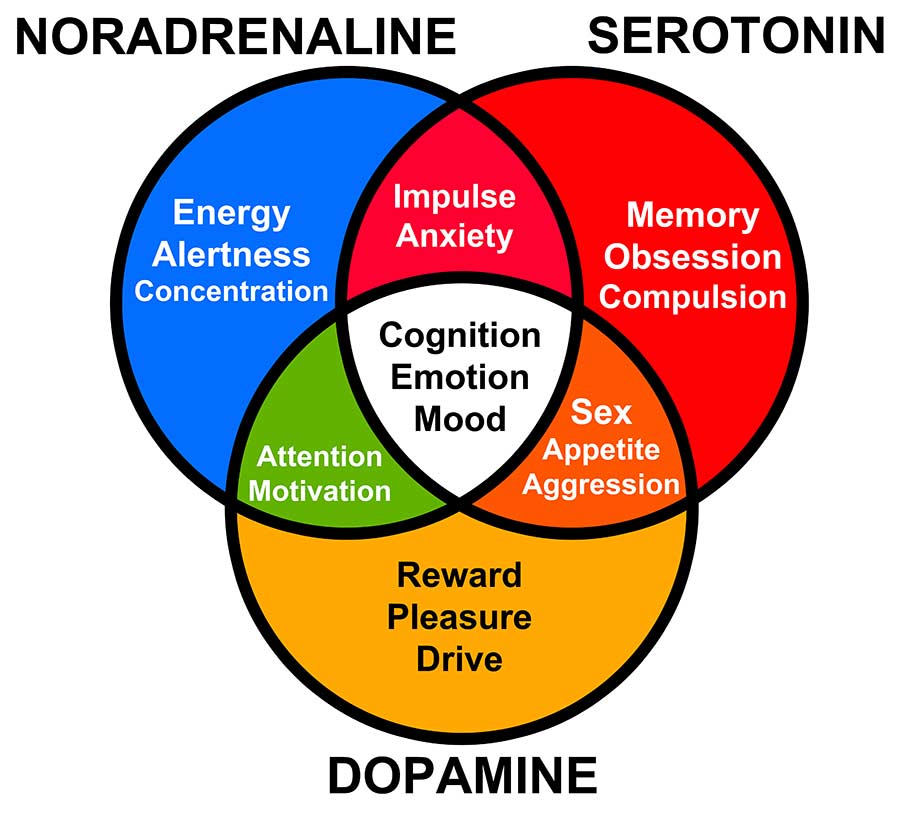
Every smoker is afraid of the nicotine withdrawal symptoms, but do you have to really worry?
The truth is, being terrified of the withdrawal prevents you from quitting. And when you experience the withdrawal and you see it as a bad thing this can make you relapse.
But when you understand why the withdrawal is good for you, you can go through it easily.
What is nicotine withdrawal?
Nicotine withdrawal happens when nicotine and toxins leave your body. Withdrawal starts around 30 to 45 minutes after you smoke a cigarette so when you’re a smoker you have withdrawal all day long.
But when you stop smoking, when you stop supplying your body with nicotine you have more intense withdrawal that eventually ends.
Some examples of nicotine withdrawal symptoms are:
- Cough
- Brain fog
- Agitation
- Smoking dreams
- Tingling in your hands and feet
- Physical and mental cravings
Of course, you’re not going to experience everything. You can learn more about the nicotine withdrawal symptoms and how to face them here.
6 Reasons to Embrace the Nicotine Withdrawal
1. Withdrawal is Detox
When you have the flu you have symptoms – like fever, you feel shaky or you feel tired, right? You have those symptoms because your body is trying to fight off the toxins and the infection.
The same thing with the nicotine withdrawal; you have symptoms because your body is fighting off the drug and the toxins. Withdrawal is detox.
2. It is Temporary
It’s not gonna last forever! The nicotine withdrawal will end as long as you stay nicotine free.
The withdrawal symptoms that you may experience can last from a couple of days to a couple of weeks.
But if you’re using nicotine substitutes or vape this is going to prolong and extend the nicotine withdrawal because you keep supplying your body with nicotine.
You don’t need to use those products. The withdrawal is not any worse than a common cold!
3. Nicotine Withdrawal Is Not Harmful. It’s Helpful
The withdrawal is not harmful to your health, it’s actually helpful!
For example, if you experience cough and chest pain this may seem bad but what really happens is that the muscles in your chest contract so they can expel all the mucus that has been accumulating in your lungs all those years. So it looks bad but it’s a good thing.
Or if you experience tingling in your hands and your feet this happens because oxygen is finally flowing properly to these areas of your body.
When you have physical cravings, it’s because you have less and less nicotine in your body.
Or if you’re feeling down or anxious after quitting smoking, it’s because your brain starts regulating dopamine – the feel good chemical in your brain – naturally so that you can feel good without needing nicotine… and your emotions will not be controlled by nicotine anymore.

Because quitting smoking, and this has been proven by research, decreases depression and anxiety even if you have chronic depression and anxiety. And it increases happiness. But for you to get those benefits, you need to go through this adjustment period that we call withdrawal.
4. Nicotine Withdrawal Is Easy to Overcome if You Change Your Mindset
In 1971, during the Vietnam War 20% of the US soldiers were addicted to heroin. And because the government was worried, they created the Special Action Office of Drug Abuse Prevention to track those soldiers and help them.
Here’s where it gets interesting! After leaving the war only 5% of the soldiers that were addicted to heroin relapsed within a year and 12% relapsed within three years.
90% of heroin addicts quit basically overnight – no withdrawals, no pains, nothing. And the researchers concluded that this happened because they changed their environment.
They went from war to home so their triggers were gone, the reasons for using were gone, and they changed how they saw their addiction.

And that’s what I want you to take from this. You need to change your context your frame of mind and your routine. Because quitting smoking is a mind game it is as big of a deal and as difficult as you make it to be. It’s all about context.
And if they can overcome heroin withdrawal you can definitely overcome nicotine withdrawal.
5) Nicotine Withdrawal Is a Sign of Health & Healing
The nicotine withdrawal is a sign of health, healing, and progress. It is a sign that your body adjusts back to normal health and a sign that you’re doing things right.

If you don’t experience any withdrawal symptoms then how do you know you’re overcoming the addiction?
Withdrawal is a sign your body is changing, it is a feedback loop, a conversation between you and your body. It’s your body telling you “Hey you did the best you could you quit smoking be patient with me I’m changing just stay away from nicotine and smoking.”
6) Nicotine Withdrawal Serves as A Reminder of Your Effort
The withdrawal is a reminder of your effort and a reminder of how many changes your body had to go through trying to heal. And if nothing else, this can make it harder for you to go back.
It’s like touching a hot stove. It’s gonna hurt a little bit but next time you’re around a hot stove you’re gonna remember your past experience and hopefully step back.
Same here, if you remember all the changes you had to make this is going to stop you from picking up a cigarette after you quit.
Now I’m not telling you you have to suffer but just remember how it felt like to be addicted.
Take Aways
You should embrace the nicotine withdrawal because:
- It’s detox and not worse than a common cold. It’s your mental state that makes all the difference.
- The withdrawal is temporary.
- It’s not harmful to your health it’s helpful.
- And it’s easy to overcome it if you change your frame of mind. If you see it as a trauma it’s gonna be painful but if you’re a happy about quitting you’re gonna see it as freedom signs. And I invite you to change its name call it “freedom signs” because the words we use change our experience. So if the name “nicotine withdrawal” has a negative connotation for you or if it makes you feel bad just change how you call it. You can call it freedom signs or something else that makes you feel empowered.
- Nicotine withdrawal is a sign of health, healing, and progress and a reminder that you don’t want to go back to smoking.
If you want to overcome the mental addiction and change how you see smoking, you can start by getting the foundational video and PDF starter guide of the CBQ Method.
The CBQ method is a 4-stage method that helps you overcome the mental addiction, change how you think about smoking, and break the habit.
Click here to get the Foundational Video if the CBQ Method
And if you want help and support, you can join our CBQ method Facebook support group. We have thousands of amazing members who are on the same journey as you, and we post tips every day to help you quit smoking and remain smoke-free.
Join the support community here: https://www.facebook.com/groups/cbqmethod/